In the technology project »Model-based development of the evaporator periphery«, the components adjacent to the evaporator are adapted so that newly developed evaporators can be profitably used in a heat pump. In order to operate the evaporator of a heat pump efficiently, certain boundary conditions must be met so that icing and defrosting as well as the equal distribution of air and refrigerant function correctly. These include that the air flow is optimally designed, that the refrigerant enters the evaporator in the correct state and that the ice slurry, which is formed in the drip tray during a defrost, can melt efficiently.
more infoProjects and References
-
-

Lärmemissionen von Wärmepumpen.
In the »MENESA« project, the three research institutes Fraunhofer ISE, Fraunhofer IBP and Fraunhofer IWU are working on methods to improve heat pumps with regard to vibrations and noise. The resulting methods allow structural-dynamic and acoustic aspects to be taken into account at an early stage in the development of heat pumps, so that low-noise operation can be achieved in a real operating environment.
more info -

Measurement of vehicle exterior noise on the vehicle test bench.
The acousticians at the Fraunhofer IBP investigate in the context of the project "Fraunhofer System Research for Electro-Mobility" the various aspects of future car concepts, and drive systems, as well as the storage and distribution of energy.
more info -

Sound screen in the semi-anechoic chamber.
The aim of the project acoustic umbrella was to design a construction that allows a simple and repeatable investigation of research objects with regard to their radiated sound power.
more info -

WAMS: Heat pumps - Acoustics and multi-source systems.
Electrically driven heat pumps and air conditioning systems are future-oriented technologies of the energy transition. For widespread use in multi-family houses or office buildings, a new generation of devices is required.
more info -
SAGA
Highlights from research and development
Sound absorbers for aggressive flue gas media.
Researchers at the Fraunhofer IBP have replaced the condensate-sensitive materials with unavoidable waste from PTFE production. In this approach, the scientists achieve sustainability in three respects.
more info -

The project aims at reducing acoustic emissions from fans.
In the project “Acoustically optimized design of fan attachments and casings (ADVentAGe)”, hybrid active noise control systems are being developed and validated in collaboration with project partners. These can be integrated into fan casings or typical fan attachments such as inlet cones, protective grilles and diffusers to significantly reduce acoustic emissions from fans.
more info -
The project aims at developing a demonstrator that can be used in operating rooms
Propofol, an intravenously administered hypnotic, has outstanding advantages over commonly used inhalational anesthetics. It is effective against post-operative nausea, does not trigger malignant hyperthermia - a potentially fatal anesthesia complication - and is not a greenhouse gas. The main disadvantage of propofol, however, is that, unlike inhalational anesthetics, its drug concentration cannot be determined during anesthesia using any clinically applicable method. Photoacoustic spectroscopy is a highly promising approach for monitoring propofol in exhaled air in a clinically applicable way.
more info -

How can precipitation runoff from non-metal roofs be used in water-sensitive cities?
In growing cities, more and more surfaces are being sealed. This increases the contact of rainwater with materials, e.g. roofs, resulting in the contamination of precipitation runoff with harmful substances. However, no clear or statistically relevant information on pollutant emissions is available for most roof materials, as hardly any studies have been carried out and these are usually based on one-off random samples. General conditions such as atmospheric influences or gutter material, are often not sufficiently described. There is therefore a considerable need for research in order to draw scientifically sound conclusions about pollutants in precipitation runoff from non-metal roofs.
more info -
C3RRO - Technology spin-off for the next generation of hygrothermal simulation
Highlights from research and development

Development of hygrothermal models and user software.
The department of Hygrothermics has developed products to answer issues relating to the heat and moisture balance of components and buildings.
more info -

Visit to the outdoor test site at Fraunhofer IBP in Holzkirchen with project partners.
The rapid economic development in Vietnam has led to changes in lifestyles and needs, accompanied by novel materials, building typologies, constructions and supply systems. This is associated with a variety of building physics challenges, especially under the demanding climate conditions. The German-Vietnamese project "CAMaRSEC" addresses these challenges through the implementation and further development of energy-efficient, resource-efficient and sustainable building practices.
more info -

Prototyp der solaren Wasserentsalzung mit Parabolspiegel und Verdampfer-Einheit auf dem Gelände des IBP in Valley.
The development of solar water desalination plants is a promising approach to sustainable water treatment in water-scarce regions. At the Fraunhofer Institute for Building Physics IBP, several projects have been carried out in order to advance this technology. The aim was to evaluate the technical feasibility, identify optimisation potential and create the basis for market maturity.
more info -

The Walkie Talkie Building in London.
Radiation concentrations due to focusing glass facades can cause material damage (for instance, failure of plastics, e.g. seals in facades) and induce annoying glare problems, which may even impair visual functions.
more info -

Untersuchung von transparenten Membran-Einhausungen auf dem Freilandversuchsgelände des Fraunhofer IBP in Holzkirchen.
Every year, numerous art objects and monuments are enclosed to protect them against the weather, typically using wooden structures. However, the resulting humid indoor climate of these enclosures promotes microbial growth and increases freeze-thaw damage, often leading to expensive restorations. The project partners have therefore developed a modular enclosure system for outdoor cultural assets exposed to the elements, using transparent membranes and an innovative ventilation system. This ensures effective moisture removal under all weather conditions and eliminates moisture as the main cause of damage. Through a self-regulating ventilation system, the enclosure maintains a drier interior climate, allowing the enclosed artifacts to dry quickly and remain dry. This prevents freeze-thaw cycles from causing damage. The modular design facilitates assembly, disassembly, and storage, so that art objects both remain visible and are better protected.
more info -

Strukturvielfalt der Wilden Klimawand.
The Wild Climate Wall is an innovative green facade system designed to enhance biodiversity and climate resilience in densely built urban environments. By integrating native wild shrubs, herbs, and grasses, along with specially selected modular habitat systems (providing breeding and nesting spaces for wild bees, birds, and bats), the Wild Climate Wall offers a unique and heterogeneous diversity of plants and structures for vertical greening.
more info -

Auch das Senckenberg Naturmuseum wird im Rahmen des Projektes untersucht.
Climate change has significant impacts on our lives. Over the next few decades, extreme weather events such as heat waves, heavy rain, and flooding will continue to increase. In addition, gradual changes such as the shifting of precipitation patterns and rising annual average temperatures with more extreme heat days in the future are expected. As part of the pilot project “Climate Adaptation in Cultural Institutions”, 20 cultural institutions, including museums, libraries, theaters, socio-cultural institutions and park facilities, are being examined with regard to their vulnerability to location-specific climate-related changes, and climate adaptation measures are being developed. Based on these assessments, tailored adaption measures will be developed, considering structural, organizational, and programmatic potentials. The project focuses not only on protecting people, but also on safeguarding the buildings themselves and their often historically valuable interiors.
more info -
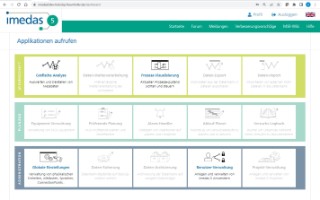
Dashboard of the IMEDAS 5 Systems.
IMEDAS is an in-house software development for measurement, control and regulation of test benches.
more info -
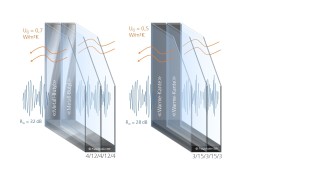
Comparison of the thermal insulation and sound insulation properties of thermal glazing.
Although modern thermal glazing reduces a building’s energy requirements, it also has an impact on sound insulation.
more info -

Fungal adhesive prototype made from cattail (lat. Typha) bound by the Ganoderma fungus.
To achieve a biological transformation, material flows must be considered as a whole and biointelligent solutions found for them. Closed material cycles are essential. For the insulating material, biological raw materials as well as residual materials are bonded together by mycelial growth.
more info -
The overall objective of the CoolDown project is to collect and validate suitable measures for the rapid and practicable transformation of heating networks with a focus on the secondary side and (existing) buildings. To this end, the technical, regulatory and economic requirements will be identified and evaluated in detail.
more info