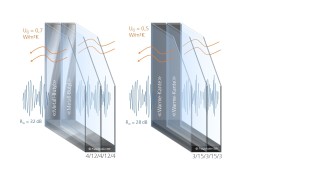
Quanderland acts as an enabler of photonic and quantum technology solutions for sustainability challenges.
The project combines innovation, technology, and sustainability in a unique research network, designed to make quantum technologies tangible, application-oriented, and future-proof. In addition to fostering new cooperation formats for idea development and rapid prototyping, the project emphasizes the robust investigation of ecological, social, and economic aspects of the applications, as well as the added value that these technologies can deliver. Fraunhofer IBP plays a central role in evaluating the potential of the investigated approaches and supports all joint projects in this funding program with expertise in life cycle assessment and sustainability evaluation.
more info