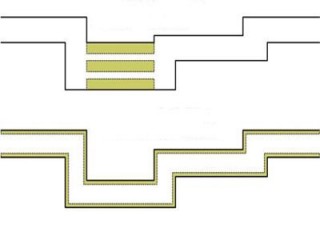
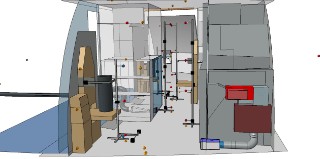
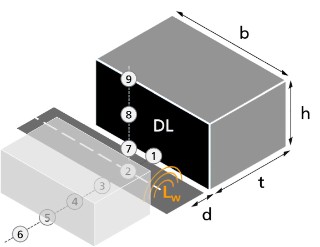
Noise transmission from building services in timber and lightweight construction.
With the growing importance of sustainable construction and increasing demands for comfort and efficiency, timber and lightweight buildings are becoming more prevalent. However, these construction types pose specific challenges in terms of noise transmission from technical building systems. To address this issue, the Fraunhofer IBP is developing the “PreNoise Wood” research project - a groundbreaking method for predicting and reducing installation noise in resource-efficient buildings. Based on the successful outcomes of the “ProSa” project for solid construction, “PreNoise Wood” adapts and extends those methods specifically for timber and lightweight structures. The goal is to create scientifically sound and practically applicable solutions, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), enabling early-stage acoustic optimization of building components and technical systems, and providing reliable planning tools for noise prediction - a clear benefit for building owners, manufacturers, and planners.
more info